How the parking sensors work: the TAPS system explained
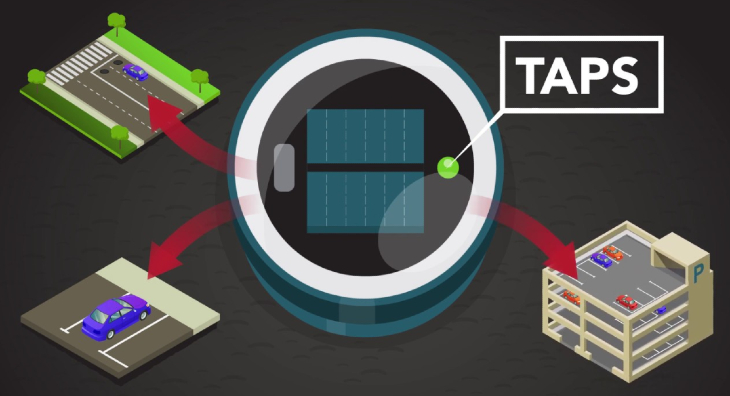
The advantages of our TAPS ground sensors for parking lot monitoring are obvious. The small, low-maintenance sensors are easy to install, energy-autonomous and exceptionally reliable with a detection accuracy of more than 99 percent. But how do parking sensors work to achieve this level of precision? In the following article, we will take a closer look at the functional principle.
How does the parking sensors work? What technology is used?
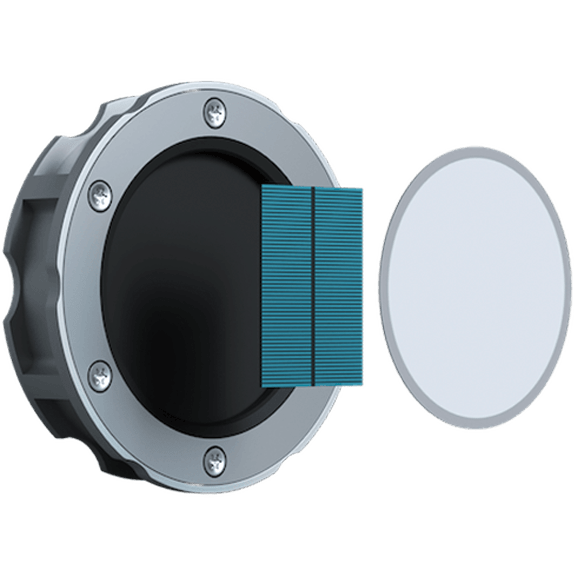
Our TAPS sensors are based on the principle of the so-called magnetoresistive effect. This physical effect has been known since the 19th century. The electrical resistance in ferromagnetic alloys changes with the variation of an external magnetic field. More precisely, the resistance changes with the angle at which a magnetic field acts on the conductor.
With current technology, even small changes in electrical resistance can be measured very accurately. Cars and other vehicles made of metal have a significant influence on magnetic fields. This fact is also exploited, for example, by induction loops, which are used in road traffic to control traffic lights that are switched according to traffic conditions.
Most induction loops used on the road, however, have a certain base load because they generate an electromagnetic field themselves. Self-sufficient induction loops, on the other hand, are much less sensitive and require an active magnetic field to pass through the loop field. In cars, for example, the alternator generates such a weak field.
Die Parkplatz Sensoren Funktionsweise des TAPS-Bodensensors erlaubt dagegen die Erkennung von Fahrzeugen auch dann, wenn Motor und Lichtmaschine abgeschaltet sind. Gleichzeitig ist die energetische Grundlast wesentlich geringer als bei einer aktiven Induktionsschleife, da lediglich die Leitfähigkeit geprüft werden muss. Der TAPS-Sensor braucht so wenig Energie, dass er sie selbst generieren kann.
Aufgrund der hohen Widerstandsfähigkeit und Zuverlässigkeit der Sensoren eignen sie sich auch zur Nutzung im Strassenverkehr. Sie sind wesentlich günstiger als Induktionsschleifen. Daher ermöglichen sie das Design smart cities and traffic management systems mit einer Vielzahl von Sensoren. The simple installation of the ground sensors

The simple mode of operation of the TAPS sensor also allows the technology to be packed into a small, compact device. This simplifies installation enormously compared to other solutions. Neither cables need to be laid nor the parking lot floor opened up over a large area. Only a single hole is required. The sensor is inserted into this hole and works independently from this point on.
The sensor's tempered safety glass protects the device from environmental influences such as rain and snow. It is also no problem if cars drive directly over the sensor. On average, our ground sensors can be used for well over ten years and require exceptionally little maintenance.
How is the data processed and transmitted by the sensor?
The TAPS sensors installed in the parking lot now detect changes in parking conditions and can store the data. But how can they be used? Using a proprietary radio standard, the sensors transmit the currently recorded data to a central gateway.
The gateway has a detection reach of up to 150 meters. It also processes the data from up to 64 ground sensors. This means that a single gateway is often sufficient to register the sensor data of an entire parking lot. For larger parking lots, there is the option to extend the range and capacity of the system.
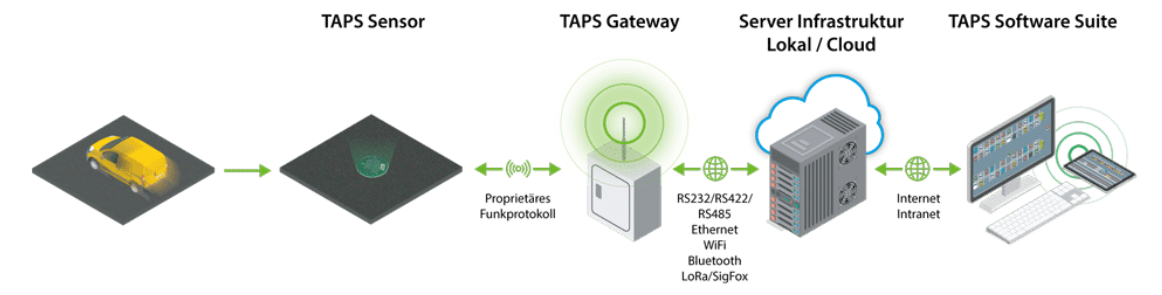
In addition, it is possible to carry out communication using a wide range of standards. These include, for example:
This means that the TAPS sensors can be used in an enormously wide range of applications.
The gateway collects the data and transmits it in the next step to the TAPS software. This is a sophisticated management application that visually displays and analyzes the utilization of the parking facility. In addition, it provides an API that allows the data to be used by other programs and devices.
What are the opportunities offered by the API of TAPS?
The API (application programming interface) of the TAPS system is of central importance. This is because it gives users of our sensors the option of further processing real-time parking space occupancy data with their own software. For example, the information can be transferred to a cloud provider for advanced analysis.
But very practical system solutions can also be implemented in this way. These include traffic lights or display panels that warn of increased parking space utilization. Even the dynamic pricing of parking spaces is conceivable.
Die sichere REST-API des TAPS-Systems gibt Daten sowohl JSON- als auch XML-formatiert aus. Software-Entwickler können so mit vielen vorgefertigten Bibliotheken darauf zugreifen und die Informationen mit geringem Aufwand weiterverarbeiten.





)
)